Microsoft Azure Backup is a simple yet powerful service that empowers customers to backup Microsoft workloads to Azure. Recovery services vaults protect:
- Azure Resource Manager-deployed VMs
- Classic VMs
- Standard storage VMs
- Premium storage VMs
- VMs running on Managed Disks
- VMs encrypted using Azure Disk Encryption, with BEK and KEK
- Application consistent backup of Windows VMs using VSS and Linux VMs using custom pre-snapshot and post-snapshot scripts
The Azure Backup service has two types of vaults: Backup vault and Recovery Services vault. The Backup vault came first with the Azure Service Manager. The Recovery Services vault came with Azure Resource Manager. As a best practice, you must use the Recovery Services vault for deployment. In this article, I will describe the following steps:
- Create a Recovery Services vault for a VM
- Set the backup policy
- Select the VMs to protect
- Run the initial backup
Azure Backup
Before starting with Azure Backup, there are two prerequisites. It is assumed that you already have:
- A current Azure subscription
- An active virtual machine deployed in Azure Resource Manager
One thing you must understand is that backing up VMs is a local process. You cannot back up VMs from one location to a Recovery Services vault located in another location. So, for every Azure location that has VMs to be backed up, at least one Recovery Services vault must exist in that location. If you need an overview of the features in Azure Backup, read the following documentation: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/backup/backup-introduction-to-azure-backup#which-azure-backup-components-should-i-use
Now, the first thing you should perform is creating a Recovery Services vault. Go to the Azure Portal, click “More services” and search for “Recovery Services vaults”:
You must click “Create Recovery Services vaults”
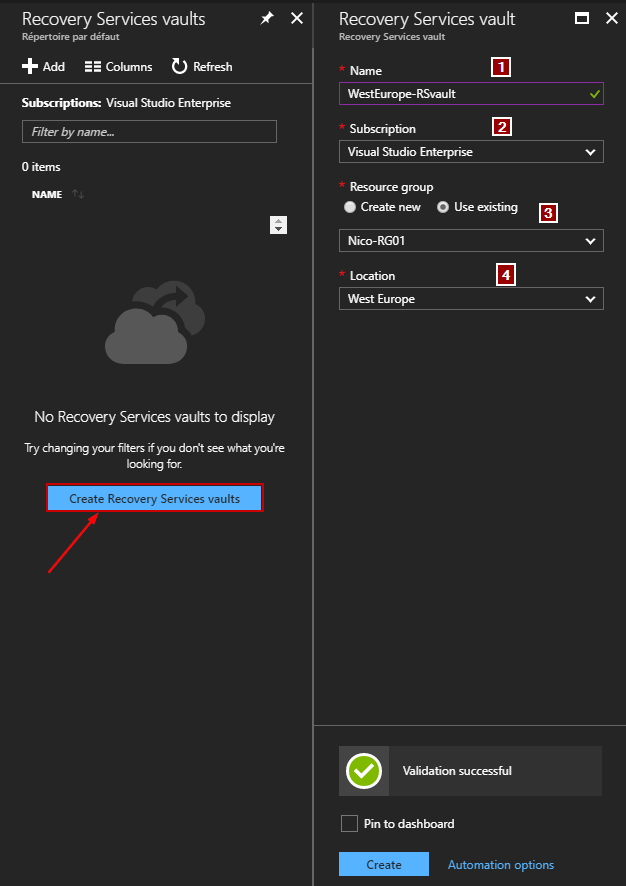
Then complete all fields:
- Enter the name
- Select your Azure subscription
- Choose an existing Resource Group or create a new one
- Select a location
Once the Recovery Services vault is created, you must create your backup policy. In the Backup Infrastructure blade, click Backup policies to open the Backup Configuration blade and click “Add”:
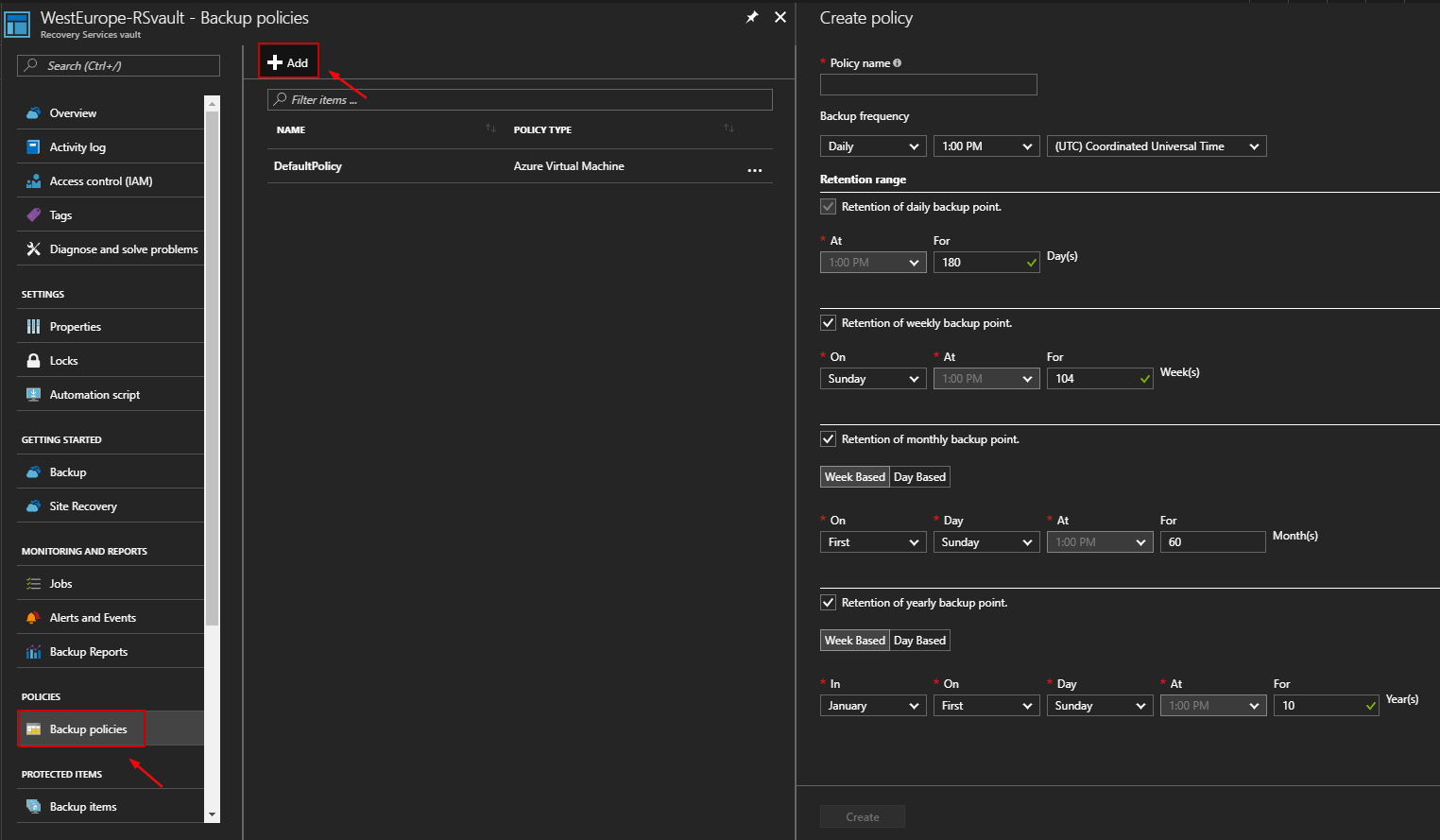
The backup policy is the schedule when recovery points are taken, and the length of time the recovery points are retained. If you need to backup files and folders, you must use the Microsoft Azure Backup agent. In my case, I want to backup a Virtual Machine with the default backup policy. Open the Virtual Machines blade, and select the VM you want to backup and click “Backup”:
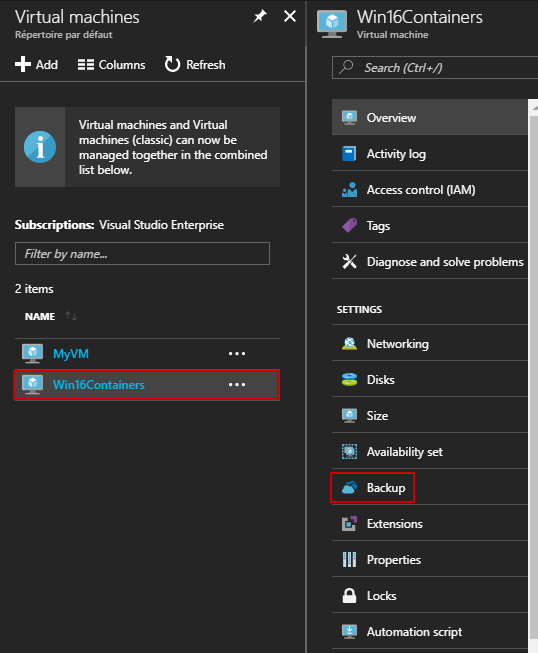
Now, I can select my Recovery Services vault called “WestEurope-RSvault” and the default policy. You also can create a new RS vault and a new backup policy at this step.
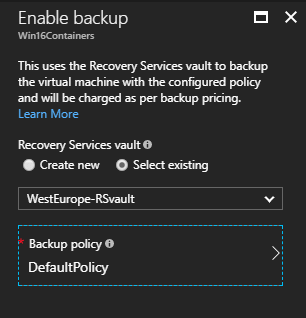
You can track the configuration progress through the notifications that appear in the portal or through the Recovery Services vault dashboard:
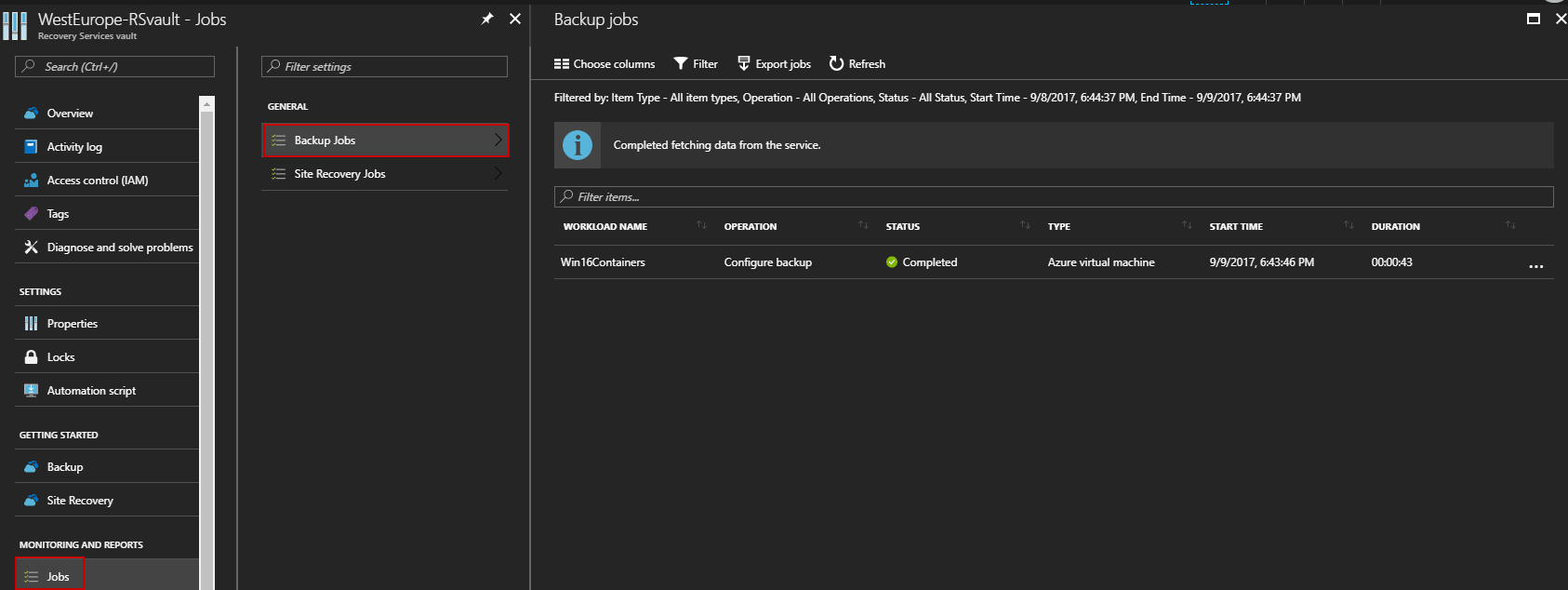
Once the backup has been defined, it will not run until the next scheduled backup is to occur. You can run the task manually if you have a requirement for the backup to be taken immediately.
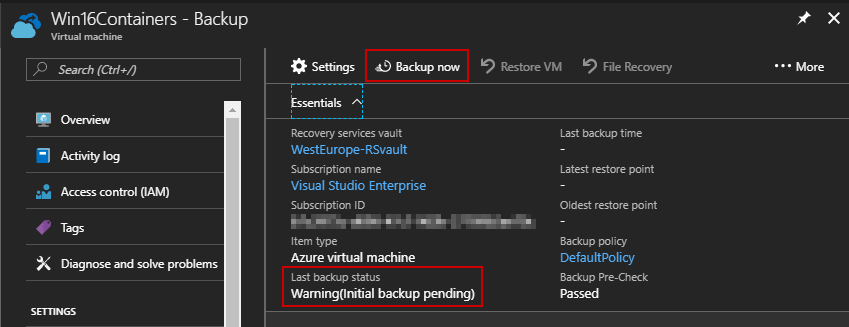
Anybody who works with Azure can easily backup a Virtual Machine even if you are a developer. That’s very useful if you plan to update a component but be careful about cost associated. Azure Backup differs from Azure Storage because it’s a service which includes bandwidth for transferring the data, the backup agent, compression and encryption.
Azure Backup and Vembu
Vembu BDR Suite provides backup and disaster recovery solution for the IT administrators running their workloads on Microsoft Azure VMs. It helps IT administrators to securely backup the Azure VMs to other regions or to other public clouds or to their data center with RTO and RPO less than 15 minutes and minimal administration effort.
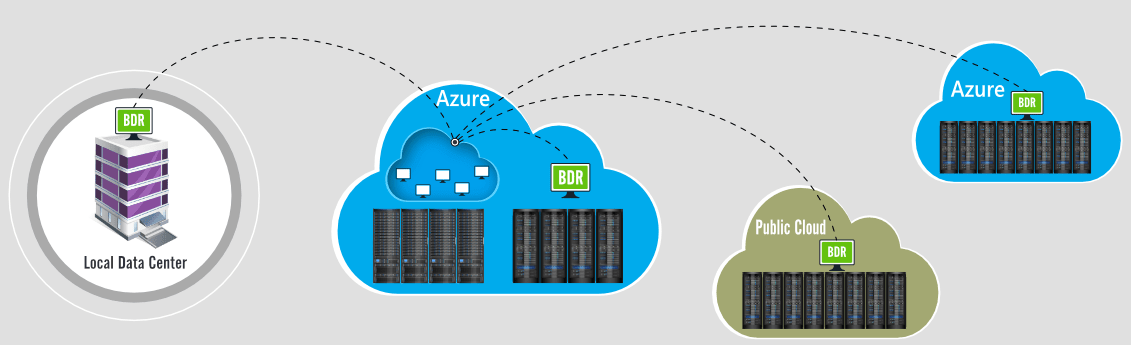
More information about Vembu and Azure Backup: https://www.bdrsuite.com/microsoft-azure-vm-backup-solution/
Azure Restore
Let’s go through the restore process. First, we need to check if the backup has been completed or not.
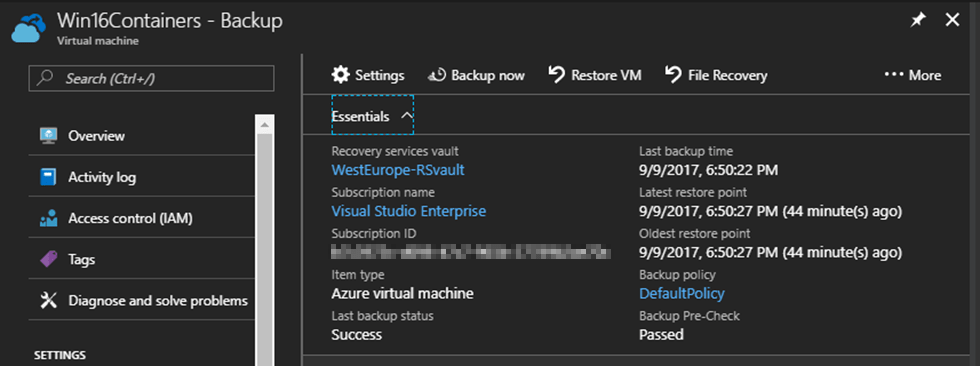
I can get more information about this backup such as:
- Last backup status
- Last backup time
- Latest restore point
- Oldest restore point
- Backup policy
- …
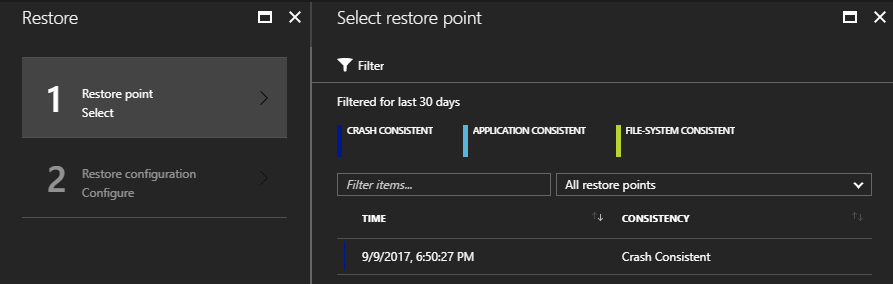
Click “Restore VM” to open the wizard. The wizard shows you the most recent restore point from which the virtual machine can be restored.
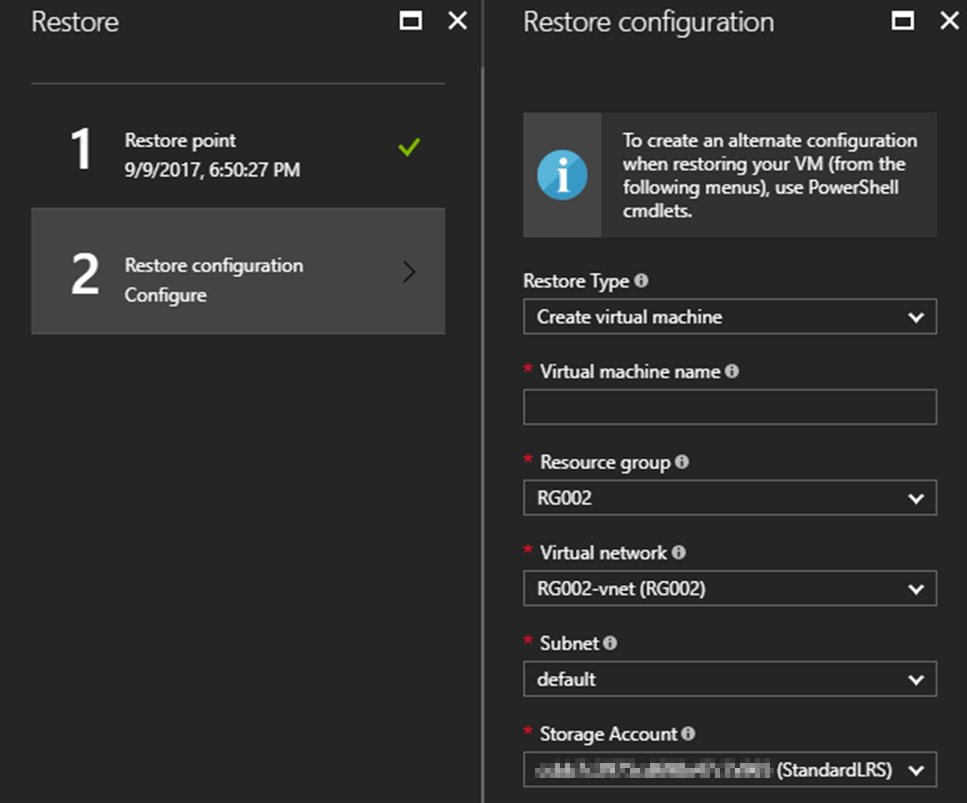
The next step is “Restore Configuration”. It allows me to define where I will restore the machine to. I can restore the machine exactly as it was, or restore it to a new resource group, a new virtual network, subnet, or to a different storage account.
The recovery from backup will start once I click the Restore button at the bottom of the wizard. Note that you can monitor the restore job in the Recovery Services vault.
Conclusion
Azure Backup is a Microsoft Azure service that you can use easily to backup and restore your data to/from Microsoft Azure. I would heavily recommend for you to start your own free trial to try it for yourself.
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.

