VMware vSphere is arguably the leader in enterprise virtualization today. Used by countless enterprises to host their business-critical workloads, it has great features and capabilities across the board when it comes to manageability, scalability, and high-availability.
While VMware vSphere features great high-availability capabilities to your customers and business stakeholders, you still must protect your data from disaster. At the heart of any good disaster recovery plan is effective backups. When it comes to backing up VMware vSphere, there are best practices you want to follow when backing up your vSphere data.
In this post, we will cover the best way to backup VMware vSphere virtual machines and consider a few key areas that you want to give attention to.
Why VMware vSphere Backups Are Important
When you look at how to protect your data from disaster in your VMware vSphere environment, the basic way to do this is with effective backups. Before taking a look at the best way to backup VMware vSphere, let’s first get an overview of what constitutes an effective backup.
There are several characteristics of an effective backup that are absolutely essential.
Effective backups include:
- Complete copies of your data
- Allow restoring all or parts of your data
- Not reliant on any part of your production infrastructure
- Keep multiple versions of your production data
- Allow properly backing up applications like Microsoft SQL Server
- Are stored in multiple locations
Other features that greatly improve not only the usability of your backups but also security include:
- Ability to encrypt your backup data both in-flight and at-rest
- Ability to replicate your data
- Ability to automatically verify the integrity and usability of the backups
- Ability to automate the process of site recovery and DR
- Ability to protect both physical and virtual resources
There are other features that you may think of in your particular environment, however, the above features are often the core essentials of what constitutes effective backups in today’s complex virtualized environments.
With the idea of effective backups in mind, we want to consider the following best practices.
- Never treat snapshots as backups
- Create image-level backups
- Create Application-aware backups
- Truncate application logs
- Use Changed-block tracking
- Encrypt backups
- Verify Backups
- Create Offsite Copies
- Use Automatic Site Recovery functionality
- Choose your Data Protection Wisely
Never Treat Snapshots as Backups
One of the innovations that virtualization introduced is the ability to take “snapshots” of a virtual machine. This allows easy rollbacks to a specific point in time of data and memory for a VM. As VMs became more prevalent and many started to use and rely on virtual capabilities like snapshots, many of these features began to be used incorrectly or for the wrong reasons.
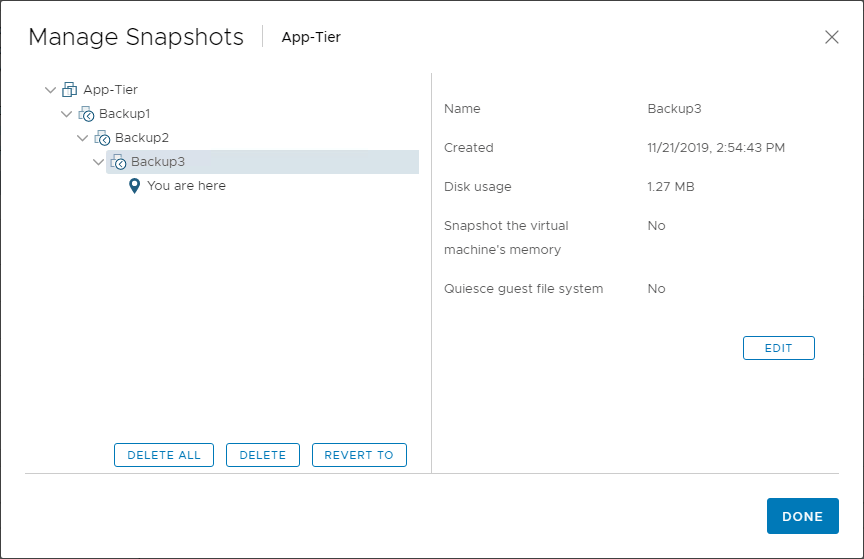
Due to the way a snapshot effectively allows rolling data back to a specific point in time, many began thinking of snapshots as a form of backup. As revolutionary as the snapshot is, it was never meant to be considered as an effective backup method for a virtual machine.
When you examine the way a snapshot works compared to the characteristics listed for what comprises an effective backup, it is easy to see why snapshots should never be used as backups.
One of the cardinal reasons that you would never want to use a snapshot as a means of backup is that snapshots rely on the underlying virtual disk structure. As mentioned above, effective backups should never rely on any part of the production infrastructure. However, this is exactly how snapshots work.
When a snapshot is taken, a delta disk is created that holds all writes to disk that is made immediately after the snapshot is taken. Without the other base virtual disk infrastructure, the snapshot data is not usable. It directly relies upon the “chain” of virtual disk files on the datastore.
In other words, a snapshot is not a complete copy of your data. It is simply a means for quick rollbacks that have specific use cases outside the realm of backups. In development or test environments, snapshots can be a great way to perform code iteration testing where code is tested on a VM and then the VM can easily be rolled back to allow further testing.
VMware best practices note that snapshots are only meant to be in place short-term (around 72 hours at most). This prevents issues related to performance, corruption, and other reasons. The bottom line is this: never treat snapshots as backups.
Create Image-Level Backups
Traditional backups in the old days most often used agents that were installed inside the operating system to perform backups of operating systems and user-specific data. Traditional backups of operating systems and data were able to create backups of the data; however, they had no knowledge of the physical hardware they were running on top of.
The age of virtualization has ushered in the “virtual hardware” construct where the physical hardware, in the case of VMware vSphere, is virtualized and presented to each VM. Performing an image-level backup of a VMware vSphere virtual machine means allows not only capturing the operating system data and any other data, but also capturing the virtual machine hardware and settings as well.
This is of key importance as it provides the ability to completely reconstruct, not only the data but the “shell” of the virtual machine that housed the data in the case where you have to perform a full restoration. This can save a tremendous amount of time and tedious effort to prevent having to manually recreate all the virtual disks and virtual hardware that may have been configured for a particular business-critical virtual machine.
To accomplish this, image-level backups in the case of VMware vSphere are taken at the ESXi host-level or more commonly, the vCenter Server level. Data protection solutions interact with the VMware vSphere Storage APIs to make image-level backups of your VMs possible.
Create Application-Aware Backups
When it comes down to it, it is not really the VMs that are important in your VMware vSphere environment, but rather, the data and applications the VMs host. Applications are the lifeblood of most organization’s business operations. Backing up your application data properly is key to protecting your application data with the highest levels of integrity.
Application data is typically hosted by applications like Microsoft SQL Server that rely on transactional consistency to avoid data corruption. Properly backing up applications like Microsoft SQL Server requires using a data protection solution that is able to properly interact with applications like SQL Server and maintain the transactional consistency they require.
In the case of Microsoft SQL Server, when a backup is taken of data on disk, there can potentially be data that exists in memory that has not been written to disk as of yet. Without properly flushing data in memory and any pending I/O operations, backups of only the data on disk make result in data corruption or inconsistency. How can consistency be maintained?
This is done properly in the case of SQL Server by using Microsoft’s Volume Shadow Copy service. Microsoft’s VSS has hooks into applications like Microsoft SQL Server, Exchange Server, and Active Directory to allow properly flushing data in memory as well as pending I/O operations to disk. This is known as taking an application-aware backup.
When application-aware backups are used, VSS is properly invoked to maintain data consistency when backups are taken of your business-critical application VMs. This also has many benefits when you have the need to restore an application VM. When the backups are taken in an application-aware, consistent manner, there are no further restore operations or tasks that need to be completed such as replaying logs, etc, before data is consistent. This saves valuable time when minutes and even seconds count for business-continuity.
Truncate Application Logs
To follow the best practice to use application-aware backups, using a backup solution that can perform application-aware backups generally allows you the ability to also truncate application logs. Most logs can be pruned once a successful backup has been taken of a database.
Effective application-aware backup solutions are able to also truncate application logs for the application such as Microsoft SQL Server. This provides great benefits such as keeping the amount of disk space used for application logging at a minimum.
Use Changed-Block Tracking
With traditional backups, the backup solution would run a full backup of your data each time the scheduled backup ran. This led to long backup windows and the need for large amounts of backup storage to house backup data.
Changed-Block Tracking (CBT) is a feature found in vSphere that helps drastically improve the efficiency in which incremental backups can be taken. Changed-Block Tracking introduced a way that backup solutions can keep track of which blocks have changed since the last backup run completed.
VMs running on ESXi hosts can track disk sectors that have changed. Virtual disk block changes are tracked from outside the virtual machines in the virtualization layer. When data protection solutions perform a backup, they can request only the blocks that have changed since the last backup or the blocks in use. This functionality is part of the vSphere APIs for Data protection.
Making use of CBT allows the most efficient use of both backup time windows as well as backup storage since it drastically reduces both the time for incremental backups to complete and the storage space required to house an incremental backup.
Encrypt Backups
Security has become a crucially important aspect in all areas of IT. This includes backups. When you think about what data is contained in a production backup, it is production data. It is sometimes easy to forget that the data contained in your backups is just as critical, sensitive, and important as your production environment as this is its source.
Protecting backup data from unauthorized access requires encrypting the data. When data is encrypted it is unable to be read by anyone without the encryption key. There are two ways that backup data needs to be encrypted – in-flight and at-rest.
In-flight encryption encrypts data as it traverses across the network. Encryption of data-at-rest means you are encrypting data stored on disk. Both are essential aspects of data encryption and ensures your data is safe both as it is moving and as it is stored.
Verify Backups
One of the most overlooked aspects of taking backups is verifying your backups. After all, if you cannot restore a backup, it is worthless. All too often, a business may be in a disaster recovery scenario only to find that backups of business-critical VMs and data are corrupted and not usable. This is a situation that you certainly do not want to be in.
One of the reasons that verifying backups is not executed is that it is a very tedious and time-consuming process when left to manual means of verification to ensure that data is good. This is where automation comes into play. When businesses have an automated means to be able to verify their backups of business-critical systems are good, this is a process that is much more likely to be given the attention that it deserves.
Choosing a data protection solution that allows automatic backup verification allows performing the verification in an automated fashion. When choosing your backup solution, this should be a key requirement to consider.
Create Offsite Copies
When designing a data protection strategy, you must think about the entire solution and how your data is protected in the whole. The industry standard is a “3-2-1” approach. This describes a solution that creates at least (3) copies of your data, stored on (2) different forms of media, and stores (1) copy offsite.
When approaching your disaster recovery and business continuity strategy using this best practice, you create an environment for your data where you greatly minimize the risk that you would ever lose data. Most likely with the odds being on your side with the 3-2-1 approach, you will have at least (1) good copy of your data stored in a location that will be accessible and that will be protected from a wide range of disasters.
In line with best practice methodology, even if you have multiple copies of your data, storing all your backups in the same physical location as your production data is a bad idea. The offsite copy of your data allows you to introduce geographic diversity in your backup storage strategy.
With the availability of cloud, businesses today have more options for offsite copies of their data than ever before. Now, if a secondary physical location is unavailable for replicating or copying data, you can easily make use of cloud storage to use as an offsite backup location for storing business-critical backups.
Another point to consider, even though cloud storage is stored on disks in cloud data centers, the “media” is arguably a different media type and many consider it as so. Using cloud storage can allow great diversity in data location since you can literally choose an entirely different region where the data is stored.
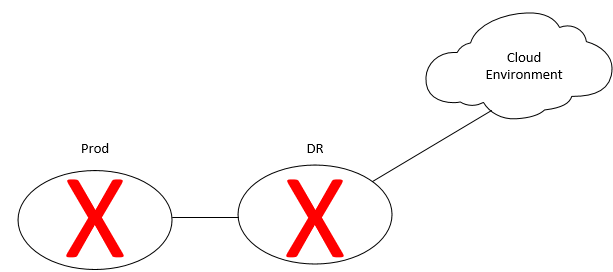
In the simple diagram below, even if you lose data in both the Prod and DR locations due to a major natural disaster affecting a region, the cloud datacenter, in another region, still has a protected copy of your data.
Use Automatic Site-Recovery Functionality
A great way to increase the resiliency of an entire site is to use replication. Using replication, you can take an exact copy of your VMware virtual machine and create a replica of that virtual machine in an entirely different location such as a DR facility. This provides protection to your data and the virtual machines themselves. This is key in that it drastically reduces the amount of time it takes to recover access to your data.
After all, if you only have the data, but do not have any of the VMs up and running to answer requests for that data, your RTO is going to be extremely poor. With replication of VMware virtual machines, you are able to have “warm” copies of your production VMs located safely in a different facility. The warm virtual machines are ready to start servicing requests for your data in times of disaster affecting your main production site.
The process to switch from your production site virtual machines servicing requests to your DR facility doing so is called failover. During a failover, connectivity for business-critical applications is switched to the alternate copies of your VMs that have been replicated to your secondary/DR facility.
But wait. Don’t the VMs that were replicated from prod have their production-site IP addresses? Yes, they do. This is where automatic site-recovery functionality by your data protection solution comes into play. With backup solutions that have automatic site-recovery functionality built into the solution, replicated virtual machines have their IP addresses changed to the new DR subnet by way of automation. During the first boot of the VM during a failover event, the IP address is correctly changed so the VM can communicate on the new subnet.
Additionally, VMware vSphere port groups are correctly assigned that can properly service the replicated virtual machines in the new DR facility. Again, this can save a tremendous amount of time during failover from the production site to the DR site. Changing IP addresses and port groups of possibly dozens or hundreds of virtual machines would not be a quick process by hand. Look for data protection solutions that have this capability built into the solution.
Choose Your Data Protection Wisely
When looking at the best way to backup virtual machines, much depends on the backup solution you choose. Your backup solution creates the framework of features and capabilities that you can use when backing up your VMware vSphere VMs.
Making a poor choice in your backup solution will certainly bring about limitations in your effectiveness in protecting your VMware vSphere environment. Choose a backup solution that will allow you to create image-level backups, application-aware backups/log truncation, use Changed-Block Tracking, encrypted backups, automatic backup verification, offsite copies, and automatic site-recovery functionality.
Having these core features will allow you to effectively protect your business-critical data in your VMware vSphere environment and meet the RPO and RTO objectives that have been defined and shaped by the needs of your business and customers.
Vembu BDR Suite – Powerful VMware vSphere Backups
Vembu BDR Suite allows you to meet all the objectives mentioned as the best way to backup VMware vSphere, it also does even more. It allows you to effectively protect your VMware vSphere virtual machines effectively and affordably.
Using the VembuHIVE file system, Vembu provides an extremely efficient, secure, compliant, scalable, and resilient way to store your backup data. In addition, no other backup vendor provides instant transition of your data easily between different virtual disk formats giving you the flexibility to transition your data between multiple hypervisors, including vSphere.
Vembu BDR Suite features include:
- The latest vSphere support
- Changed Block Tracking
- VMware Hot-Add and SAN transport mode
- Application-aware backups
- Compression and encryption
- Instant file recovery
- Vembu Universal Recovery
- Quick VM Recovery
- Automated Backup verification
- Offsite copies to your DR or the Vembu Cloud
With these and other features, Vembu represents a top-notch solution for backing up your VMware vSphere environment with ease of use and robust features.
Concluding Thoughts
Despite the great features offered by VMware vSphere’s ESXi hypervisor, you still want to protect your data at all costs. This includes giving due attention to features and functionality in your data protection solution to allow adhering to the best way to backup VMware vSphere.
This includes image-level backups, application-aware backups, encrypted backups, and backup verification, just to name a few. Vembu BDR Suite provides you with great options to protect your data end-to-end. This includes efficient backups, replication, offsite copies, and instant flexibility to access your disks in a number of different hypervisor formats.
Be sure and download a fully-functional free trial version of Vembu BDR Suite here.
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.

